Shoulder pain is a challenge that affects daily life more than most people realize. The shoulder is a complex joint that supports a wide range of motion, making it vulnerable to injury and strain. Pain in this area can stem from various causes such as injury, wear and tear, inflammation, or degenerative conditions. Understanding the root of the problem is the first step toward lasting relief. This guide will walk through approaches for managing shoulder pain, treatments to explore, and steps to avoid further injury.
Understanding Common Shoulder Problems
The shoulder joint consists of bones, muscles, tendons, and ligaments that work together to allow movement. Injuries or conditions affecting any of these components can produce discomfort. Common issues include rotator cuff tears, tendonitis, bursitis, frozen shoulder, and arthritis. Pain may arise gradually or suddenly, depending on the cause. Overuse injuries develop over time and are common in people who perform repetitive motions, such as athletes or workers engaged in manual labor. Sudden injuries often happen during falls or accidents. Recognizing the symptoms early can prevent worsening conditions. Persistent shoulder pain calls for evaluation by a medical professional. Imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound may be needed to identify the exact cause. Treatment options range from simple rest and physical therapy to advanced procedures.
Non-Surgical Approaches to Shoulder Pain
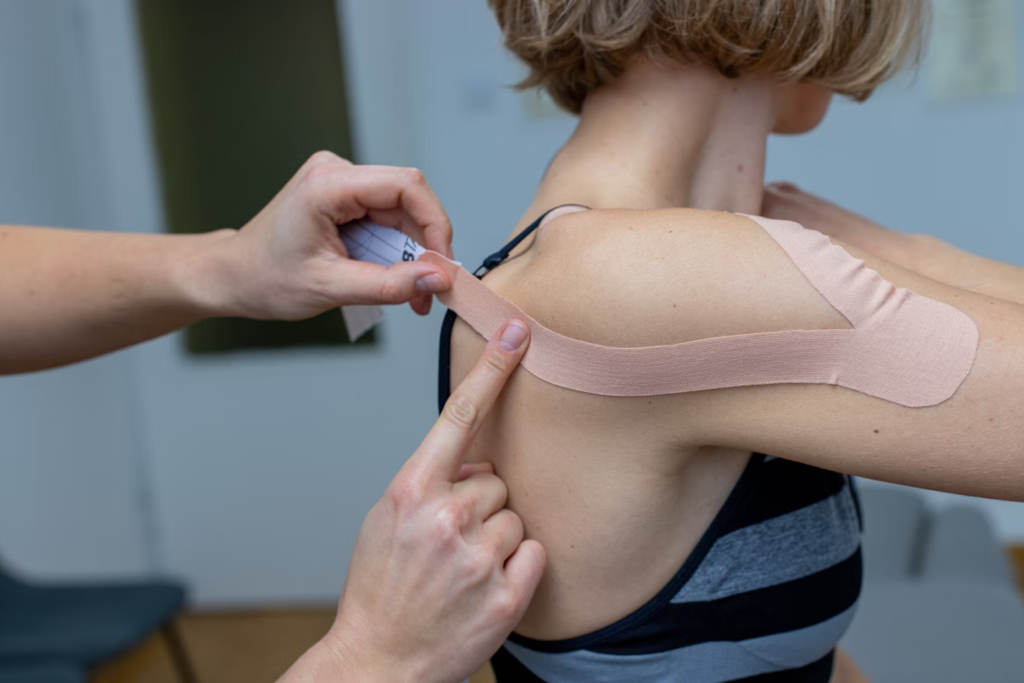
Before considering surgery, many people try non-invasive treatments to address shoulder issues. Physical therapy is often the first line of defense, providing exercises designed to strengthen shoulder muscles, improve flexibility, and stabilize the joint. These exercises can relieve pain, increase range of motion, and reduce the risk of further injury.
Pain management techniques such as heat therapy, ice packs, and anti-inflammatory medication can also ease discomfort. Applying cold can reduce swelling in acute injuries, while heat may relax stiff muscles. Occupational adjustments, such as modifying posture at work or adjusting sleeping positions, can support recovery.
Surgical Options and Recovery Process
When conservative treatments fail to provide relief, surgery might be recommended. This can include procedures to repair torn tissues, remove inflamed structures, or even replace joint components. For arthritis sufferers, surgical interventions such as shoulder replacement are often a viable option. In particular, Arthritis relief through shoulder surgery is a solution that not only targets the source of pain but also restores mobility that has been diminished by wear and tear. This surgery involves replacing damaged parts of the shoulder with artificial components, reducing friction and improving joint performance. Recovery time varies depending on the complexity of the procedure, but generally involves several weeks to months of physical rehabilitation.
Surgical recovery requires patience and dedication. Patients need to follow post-operative protocols closely to ensure proper healing. Physical therapy plays a central role in regaining strength and motion. Pain management strategies remain important during recovery, and regular follow-up visits help monitor progress.
Preventing Shoulder Pain Before It Starts
Prevention is a powerful tool in avoiding shoulder issues. Maintaining muscle strength and flexibility can reduce the risk of injury. This can be achieved through a consistent exercise program focusing on shoulder stability, stretching, and core strength. Warm-up routines before physical activity can prepare muscles and joints for movement, lowering the chance of injury.
Ergonomics at work and at home also play a role in prevention. Simple changes such as adjusting computer monitor height, using supportive chairs, or ensuring proper lifting techniques can alleviate strain on the shoulder joint.
Balancing activity with recovery is essential. Overtraining or repetitive strain without adequate rest can trigger chronic conditions. Listening to your body and addressing discomfort early may prevent long-term damage.
Nutrition and Lifestyle for Shoulder Health

https://unsplash.com/photos/poached-egg-with-vegetables-and-tomatoes-on-blue-plate-jUPOXXRNdcA
Diet and lifestyle choices impact joint health. A diet rich in nutrients that support connective tissue and bone health can contribute to shoulder wellness. Foods containing omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, and protein can strengthen joints and reduce inflammation.
Hydration is another factor often overlooked. Joints require fluid to function properly, and staying hydrated supports cartilage health. Limiting processed foods and sugars can also reduce inflammation that worsens joint pain.
When to Seek Professional Help
Recognizing when shoulder pain needs medical attention is critical. Seek a doctor’s advice if pain persists beyond a few weeks, worsens over time, or is accompanied by swelling, weakness, numbness, or limited motion. Sudden severe pain following an injury should be addressed immediately.
A professional evaluation can pinpoint the cause of pain and help create a treatment plan. Early intervention may prevent more serious damage and make recovery faster. Whether the solution involves physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, or surgery, expert guidance is key to regaining function and comfort.
Addressing shoulder pain requires understanding the cause, exploring treatment options, and making adjustments to prevent further issues. Taking action now can prevent prolonged pain and help you reclaim ease of movement for years to come.